OppositeChargesRepel_wbg.png
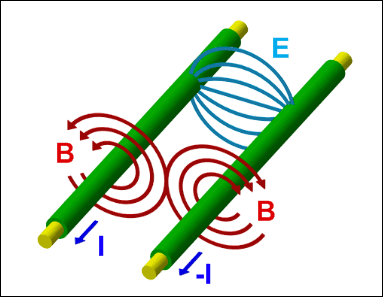
Opposite charges (I) traveling in the same direction generate opposing magnetic fields (B). At relativistic speeds, these approach the strength of the electric field (E) that attracts the opposite charges, which means that B can separate the charges into two parallel streams.