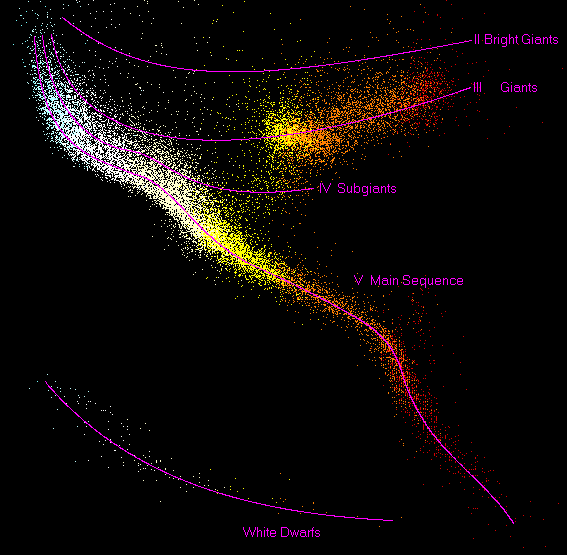
Figure 1.
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
In the standard model, after a star forms, it pretty much stays the same, until the day it blows up in a supernova. Other models contend that a star evolves over time, sliding down the main sequence. So it might be born a blue giant, but it will die as a red dwarf, where the evolution is driven by mass loss.
Jeffrey Wolynski contends that stellar evolution continues on into the brown dwarf stage, on the border between a star and a planet, and eventually, the aging star is a planet. In other words, planets are just the cores of old stars.
Conversely, some models contend that stars continue to grow, perhaps sliding up the main sequence, getting brighter and hotter as they go.
Other models maintain that Red Giants are stars in the process of being born, where the collapsing dusty plasmas have just begun to luminesce. After wavering in intensity as Cepheid Variables, they finally stabilize somewhere on the main sequence, typically at the brighter/bluer end.